SIP-167: L2 Bridged Governance
| Author | |
|---|---|
| Status | Implemented |
| Type | Governance |
| Network | Optimism |
| Implementor | JJ |
| Release | Menkalinan |
| Created | 2021-07-13 |
Simple Summary
Add the ability to govern L2 contracts with a MultiSig (Gnosis Safe) contract instead of using EOA (Externally Owned Account).
Abstract
This SIP proposes the addition of a bridge to connect L2 contracts to an L1 Gnosis Safe. The bridge will allow the ProtocolDAO to execute actions on L2 contracts using the same mechanism used on L1.
Motivation
Currently L2 contracts are owned by EAO which poses a risk on ownership and security. The proposed SIP allows a contract or MultiSig to own L2 contracts and enable proper council governance.
Specification
Overview
The proposed solution is to add a bridge contract that will act as liaison between a Gnosis Safe on L1 and the contracts on L2 so that all operations (ownership authorizations on L1 and L2) are initiated by the council on the same network, using the same tools.
Rationale
During previous discussions, we identified three different options to provide MultiSig usage on L2, each with its own pros and cons that are shown below.
-
Gnosis Safe in L1 and Gnosis Safe in L2
Pros: Same proven mechanism as in L1.
Cons: Not yet officially available on L2 (there are some forks); will require the ProtocolDAO to operate on two diferent instances/networks.
-
Gnosis Safe in L1 and Legacy Gnosis MultiSig in L2
Pros: Easy to implement.
Cons: Using a legacy MultiSig that is not supported by Gnosis anymore (there is a working project adapting it to L2, by ScopeLift); will require ProtocolDAO to operate on two diferent instances/networks, and use different tools.
-
Gnosis Safe in L1 and an Ownership Bridge in L2
Pros: Using a single tool on L1 and L2 (Gnosis Safe on L1).
Cons: Authorizations on L2 will take time due to the bridge propagation process.
From the three options the chosen one is the 3rd which, based on Gnosis Safe in L1 to perform all executions (on L1 and L2), will simplify operations. It requires the addition of a bridge (based on this CrossChainAccount technique).
Technical Specification
The proposal includes the creation of two new governance contracts that will act as bridges (OwnerRelayOnEthereum.sol and OwnerRelayOnOptimism.sol) and extend the ownwership from L1 to L2. OwnerRelayOnEthereum is owned by the Gnosis safe contract, staged transations on Gnosis Safe are directed to that contract, encoded with the appropriate data, and targeted to interact with the appropriate contract on L2. Once signed and executed by the ProtocolDAO, the L1 transaction will automatically relay to OwnerRelayOnOptimism on L2, which is the L2 owner, and will ultimately execute the commands (as owner) on behalf of the ProtocolDAO to transact on Optimism.
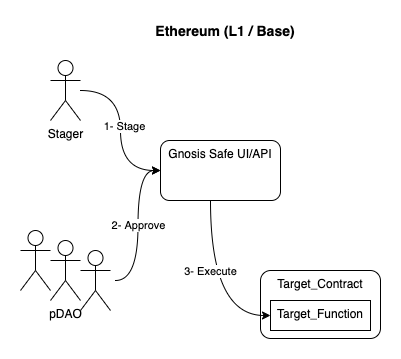
Current process on Ethereum
Ownership protected contracts on Ethereum are owned by a Gnosis Safe contract. The process of signing and executing a transaction on the protected contracts involves the staging of a transaction, the later approval from the ProtocolDAO, and its execution.
Current process on Optimism
Ownership protected contracts on Optimism are owned by an EOA, and hence, transactions can be signed directly by the holder of the associated private key.
As can be seen in the following image, optmimism contracts are more susceptible to security (based on ownership) issues and lacks the on-contract approval process.
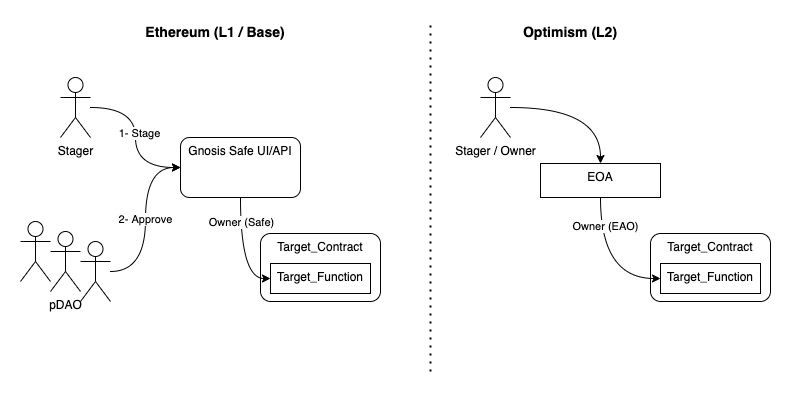
Bridged process on Optimism
In order to solve these issues, the proposal is to add a couple of contracts (one on each network, Ethereum and Optmism) that will be used as a bridge and link the Gnosis Safe on L1 to L2 owned contracts, named OwnerRelayOnEthereum and OwnerRelayOnOptimism respectively. OwnerRelayOnEthereum will be deployed in Etherum and will be owned by the Gnosis Safe contract. It will relay the transactions data to its counterpart contract on Optimism, named OwnerRelayOnOptimism. OwnerRelayOnOptimism will be the owner of the owned protected contracts on L2, so that the same protection (and same mechanism to sign transactions) that exists on Ethereum is present on Optimism.
The bridged governance solution proposed is based on CrossChainAccount technique.
The setup comprises deploying the two new contracts (one per network), linking them, and transferring the ownership of protected contracts on L2 to the relay contract on Optmism.
The following image shows the process to sign a transaction on L2, which can be split in the following steps:
- 1- Stage. A CC (Core Contributor) will stage the transaction on the Gnosis safe UI/API with the encoded data to be executed on the target L2 contract. The CC will communicate to the ProtocolDAO representatives and ask them to sign the transaction.
- 2- Approve. Once the minimum number of approvals is reached on Gnosis safe, the transaction can be executed.
- 3- Execute. The execution means the Gnosis Safe will execute the approved transaction on the OwnerRelayOnEthereum contract. Up to this point, the process is the usual.
- 4- Relay. This step is split in two (4.1 and 4.2).
- 4.1- Relay L1. The L1 part of the relay consists on sending a transaction to the Optimism Messenger from the Ethereum network that will relay it to the Optimism network. The target for this transaction is the relay counterpart on L2 (OwnerRelayOnOptimism).
- 4.2- Relay on L2. After 5 to 8 minutes, when the transaction is relayed by the Optimism messenger to L2, the transaction will be received by OwnerRelayOnOptimism.
- 5- Execute. This is actually the execution of the staged transaction on Gnosis Safe, but on a protected contract on L2.
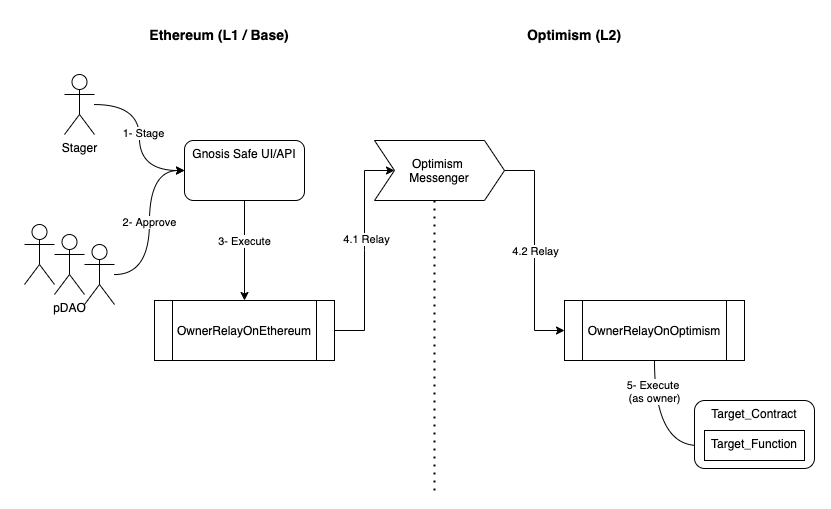
As it can be seen on the descriptions, the first steps (human involved process, from 1 to 3) are the same for signing transactions on L1 and L2, the only difference is on how to set the data and target on the staged transaction. The rest of the process is fully automated.
Test Cases
Unit Tests
Two new unit tests are added to test the two new contracts. These tests will mock the required external interfaces (i.e. opt messenger).
For OwnerRelayOnEthereum
- It reverts transactions coming from a non-owner address
- It can initiate a relay transaction to L2
- It emits an event when the transaction is relayed to the Opt. Messenger
- The data, target relayed are right
- The CrossDomainGasLimit is set to the desired value
- The CrossDomainGasLimit is set to the DEFAULT value is set to 0
For OwnerRelayOnOptimism
- It reverts transactions not comming from the Optimism messenger
- It reverts transaction originated by an L1 address that is not OwnerRelayOnEthereum
- It can accept ownership on the target contracts on L2
- It can finalize a relay transaction from L1
- An event is emitted
- The data and target relayed are right
Integration Tests
One integration test to cover the relay. Using SystemSettingsL2 as target contract on L2 and updating a setting (minimumStakeTime)
- Transfer ownership of the L2 target contract (using SystemSettingsL2) to OwnerRelayOnOptimism if still owned by an EOA.
- Try to update a setting on the target contract on L2 using a transaction initiated in L1 (we are not using a Gnosis Safe account as owner of OwnerRelayOnEthereum, but an EOA) and revert the change to the original value.
- Relinquish ownership of the target contract and transfer it back to a EOA.
Manual Tests
- Test on Kovan using fresh instances.
- Deploy and test on Mainnet.
Configurable Values (Via SCCP)
N/A at the moment of writing this SIP.
Copyright
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.